Can robots provide data on toxic cyanobacteria in lakes?
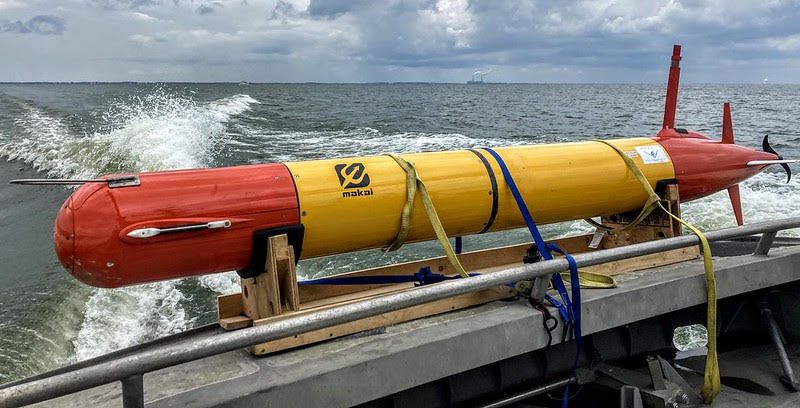
Blooms of toxic cyanobacteria can impact human and ecosystem health and have led to the death of pets and livestock. Providing accurate and frequent measurements of toxins associated with cyanobacteria harmful algal blooms (HABs) is important for public health and also can impact local economies. Traditional toxin sampling is ship or shore based, and requires several people to be involved and good weather conditions. A new system developed by NOAA and partners offers a robotic alternative that could solve many of the problems associated with traditional sampling and might help develop more detailed warning systems and forecasts for lake communities.
Can robots provide data on toxic cyanobacteria in lakes? Read More >