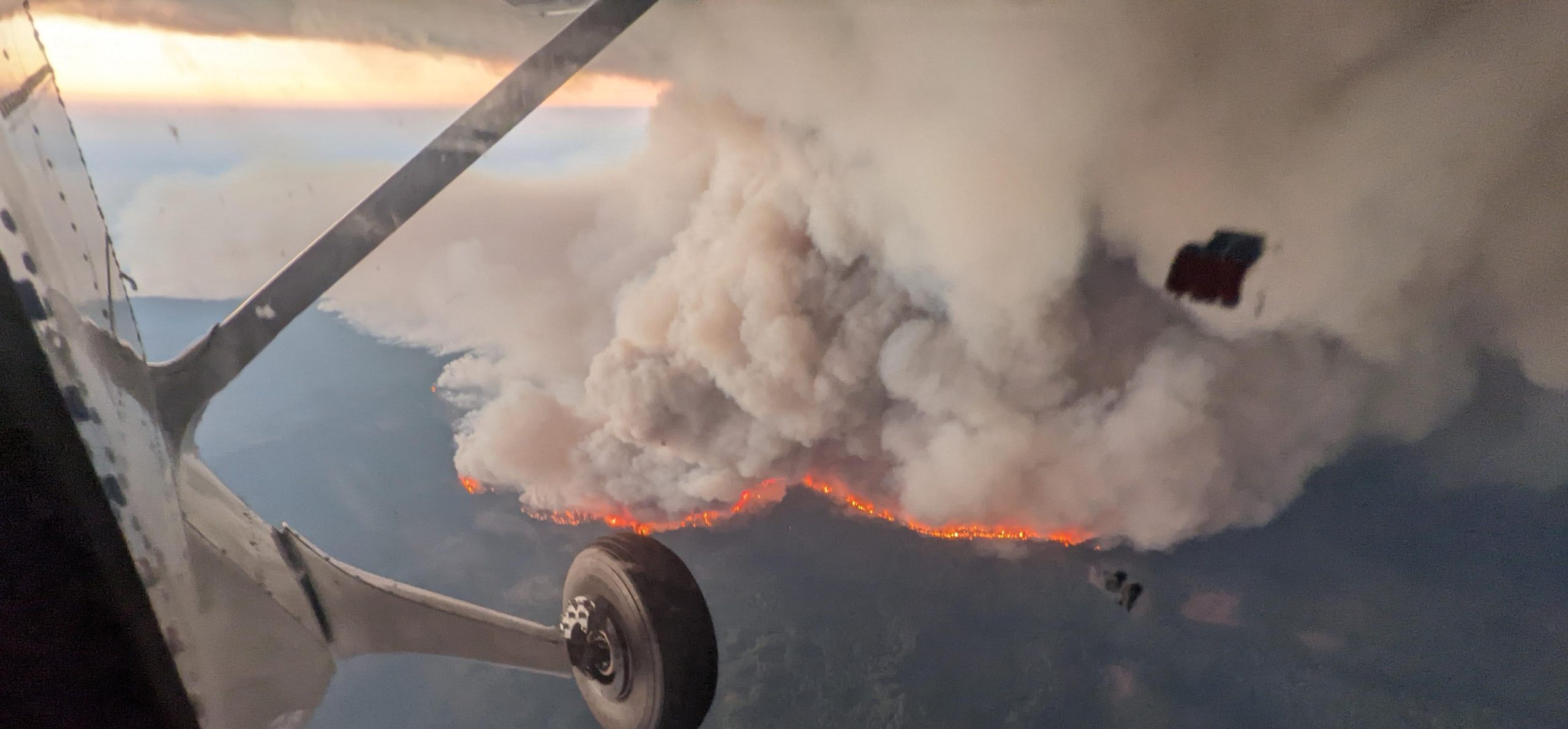
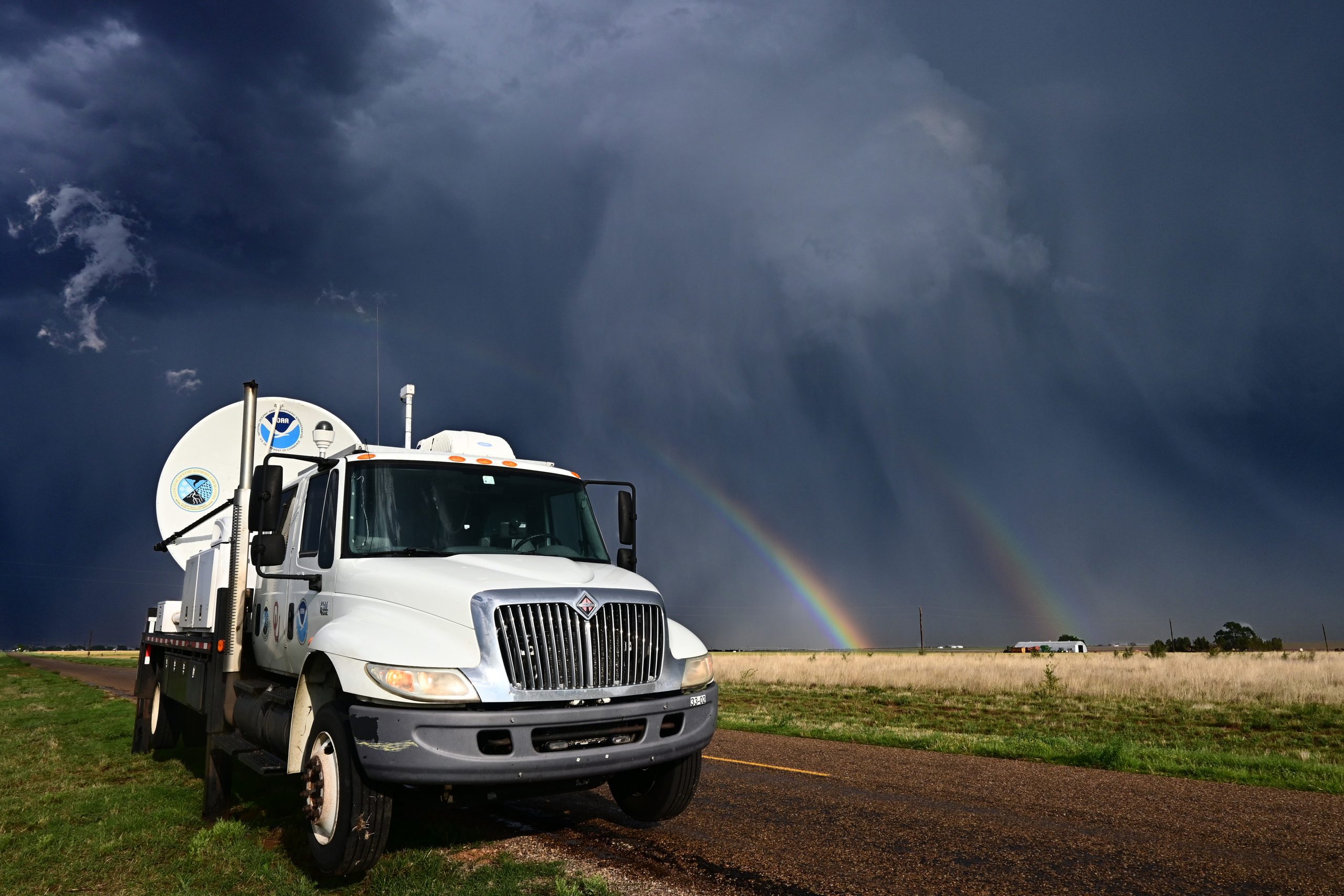
Historic flooding, a record-breaking tornado outbreak and devastating wildfire activity made April 2011 a month of historic climate extremes across much of the United States, according to scientists at NOAA’s National Climatic Data Center (NCDC) in Asheville, N.C.
Scroll to Top
Popup Call to Action
A prompt with more information on your call to action.