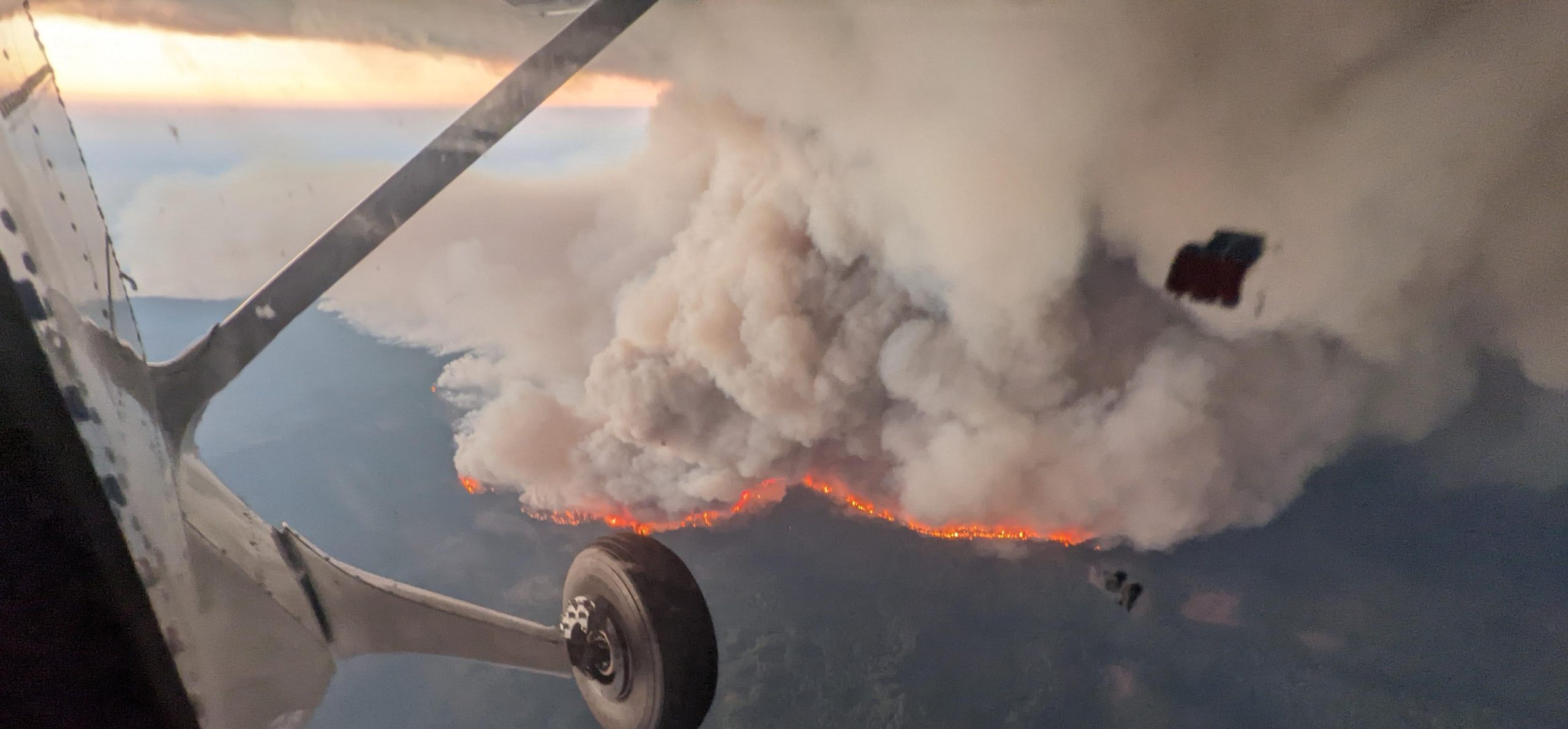
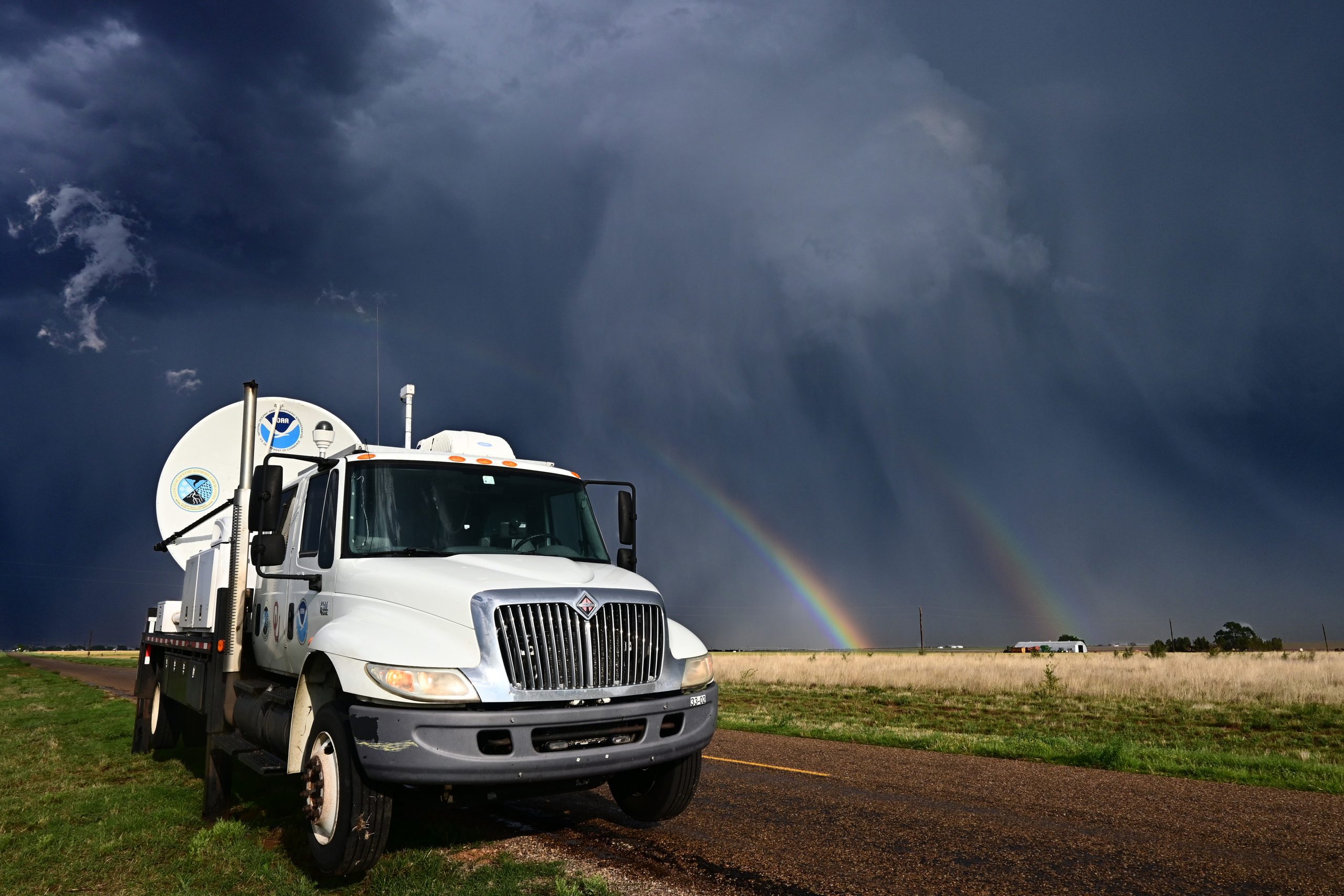
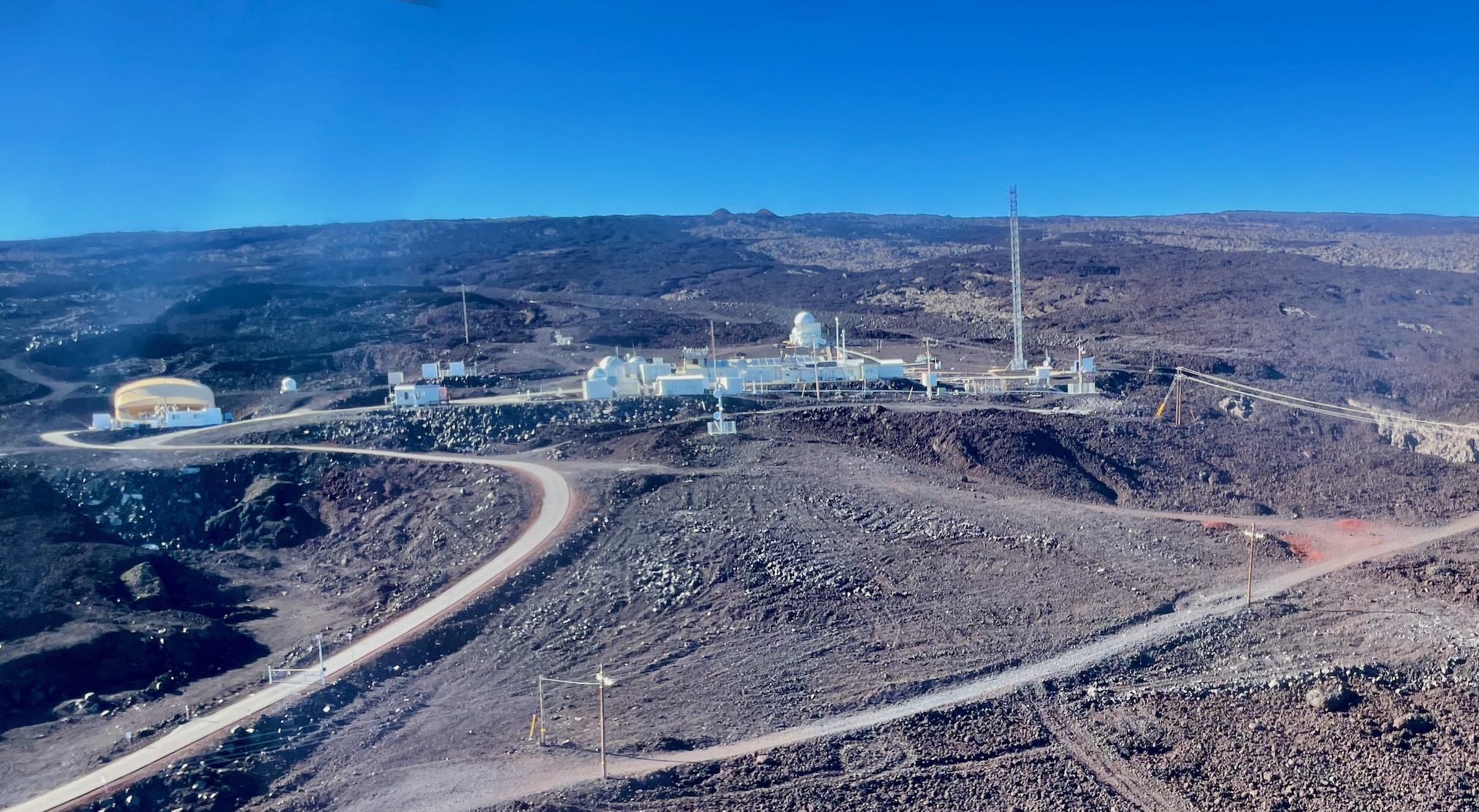
This week, the National Weather Service completed the dual-polarization technology update in Brownsville, Texas – concluding the 122 NWS radar site upgrades throughout the country. This new advanced technology is helping federal weather forecasters more accurately track, assess and warn the public of approaching high-impact weather.
Scroll to Top
Popup Call to Action
A prompt with more information on your call to action.