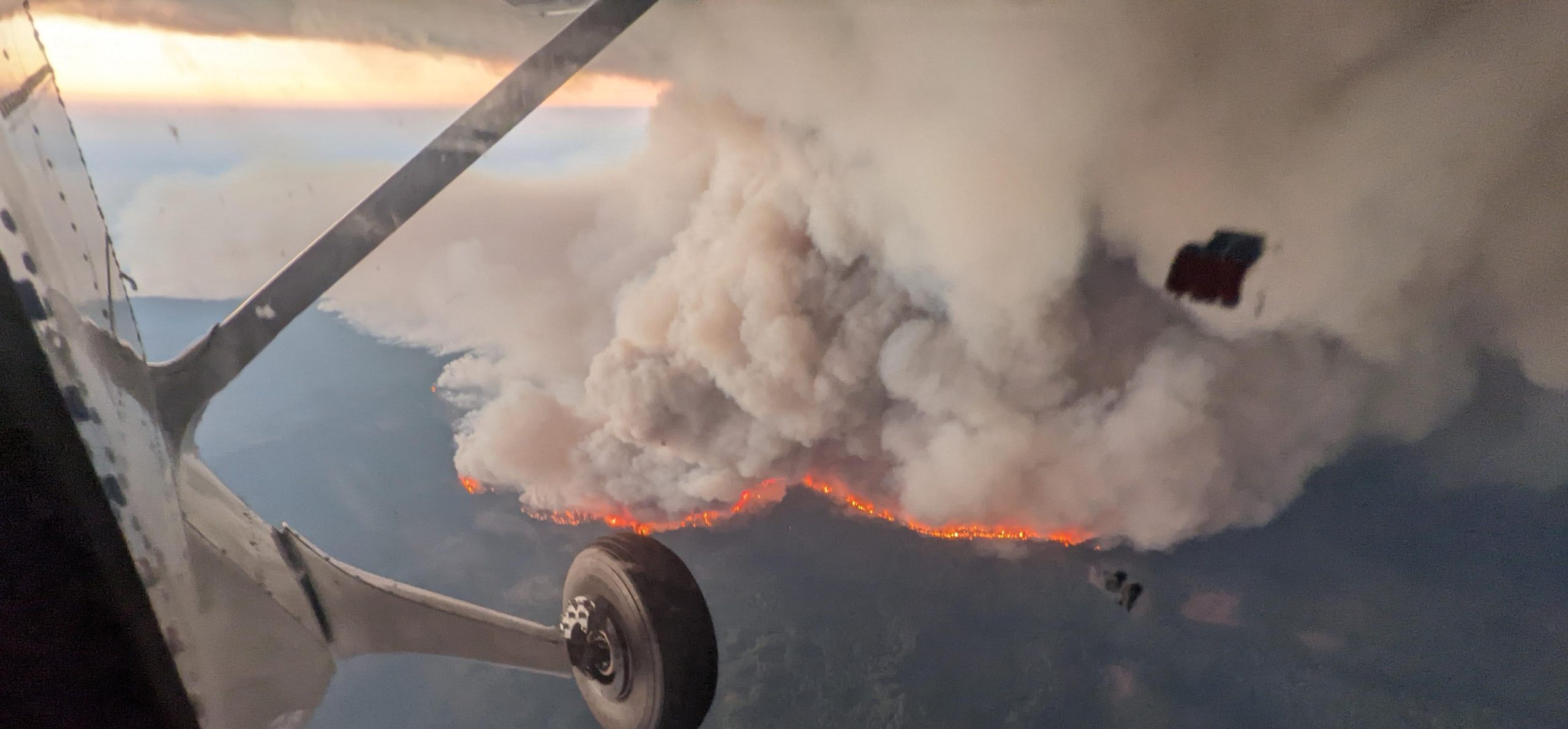
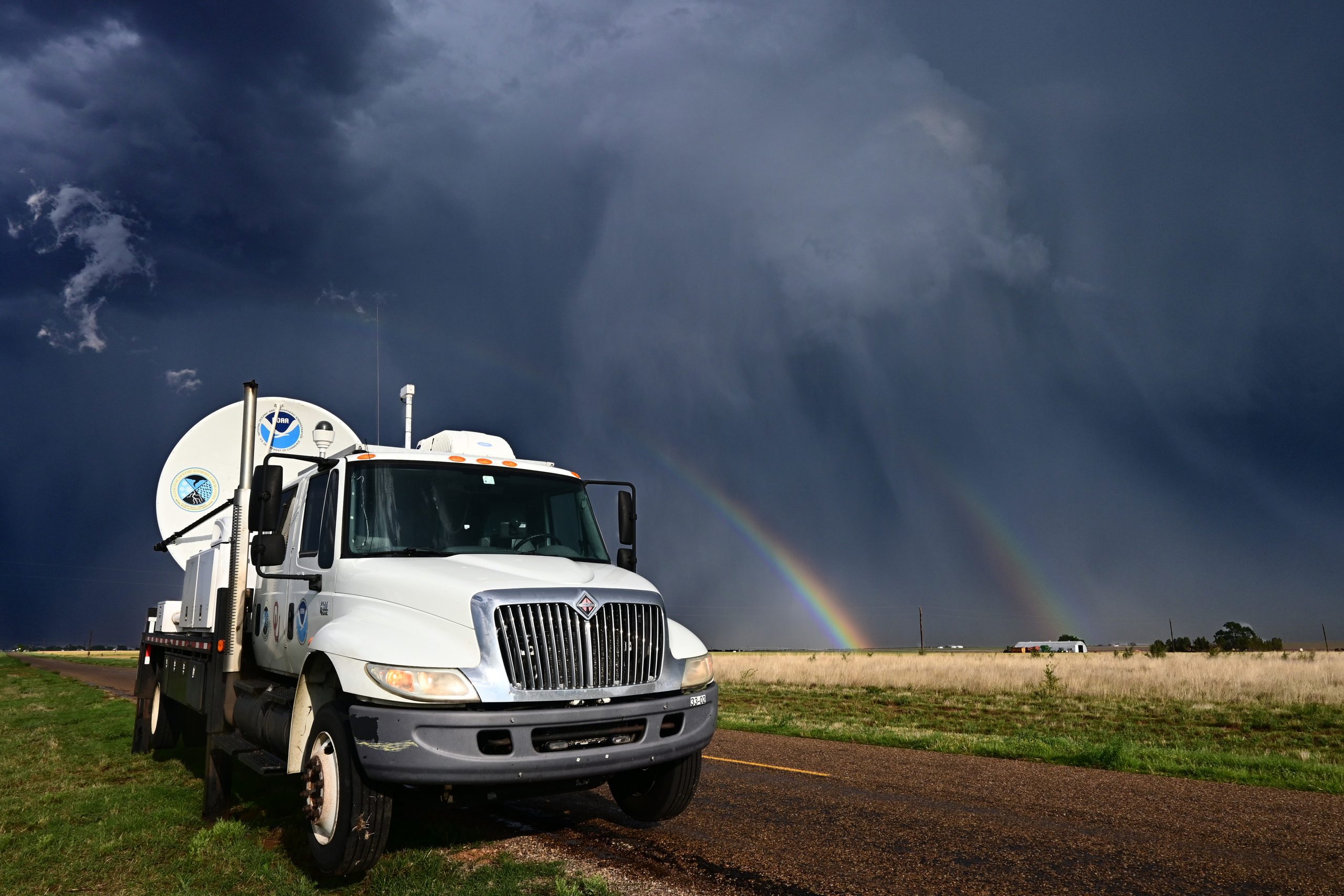
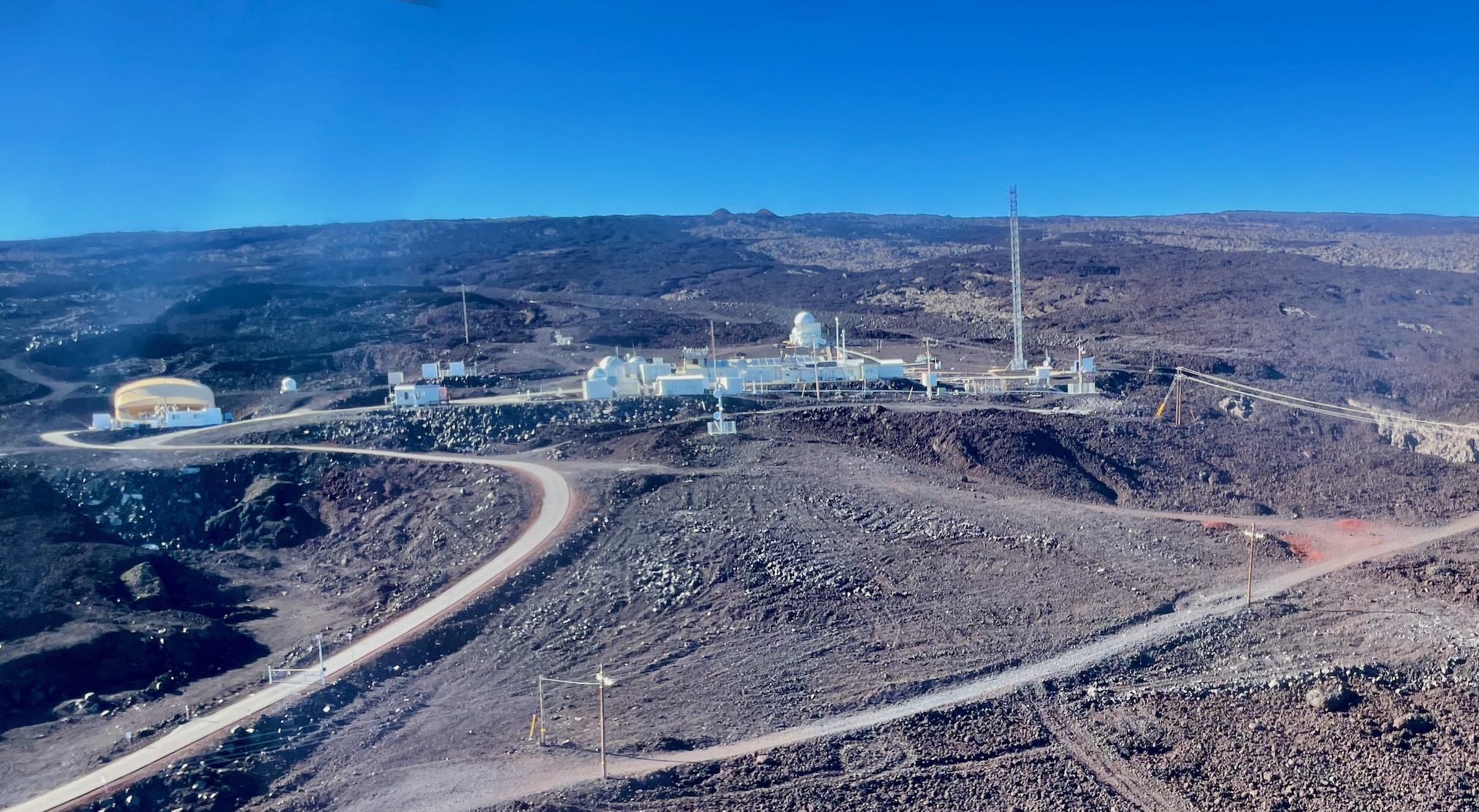
According to NOAA scientists, 2010 tied with 2005 as the warmest year of the global surface temperature record, beginning in 1880. This was the 34th consecutive year with global temperatures above the 20th century average. For the contiguous United States alone, the 2010 average annual temperature was above normal, resulting in the 23rd warmest year on record.
Scroll to Top
Popup Call to Action
A prompt with more information on your call to action.